This article identifies and short briefing of the scrum, key benefits of Scrum, and the Scrum practices that produce them.
Overview of Scrum
A Scrum is the most generally used Agile framework for creating and overseeing complex software and product applications. In its least difficult terms, Scrum is portrayed by its guiding principle of Plan Ahead, Examine and Adapt. Thus, Scrum effectively manage projects in which there is marked uncertainty and ambiguity at the beginning phases of the project.
Projects are affected by the requirements of time, cost, scope, quality, and resources, authoritative abilities that make them difficult to plan, execute, manage, and at last succeed.
The main aim is to deliver value to the customer early and continuously throughout the lifecycle of the project. To this end, those features and product increments that provide the most value for the customer are ordered so that they are developed and delivered first.
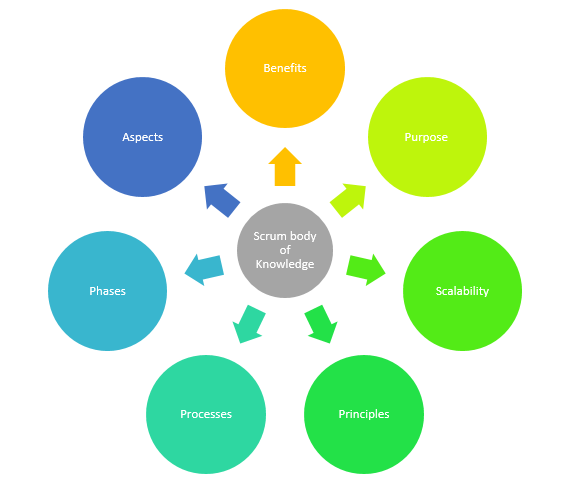
What is Scrum?
Scrum is one of the most popular agile framework. It is an adaptive, iterative, fast, flexible, and effective framework designed to deliver significant value quickly and throughout a project. Scrum ensures transparency in communication and creates an environment of collective accountability and continuous progress.
The Scrum framework, as defined in the SBOK™ Guide, is structured in such a way that it supports product and service development in all types of industries and in any type of project, irrespective of its complexity.
Overview of the initiate phase in Scrum
Initiate phase, as defined in A Guide to the Scrum Body of Knowledge (SBOK™ Guide), is applicable to the following:
- Portfolios, programs, and/or projects in any industry
- Products, services, or any other results to be delivered to stakeholders
- Projects of any size or complexity
The Initiate phase processes and their objectives are listed below:
- Create Project Vision
- Identify Scrum Master and Stakeholders
- From Scrum Team
- Develop Epics
- Create Prioritized Product Backlog
- Conduct Release Planning
Quote

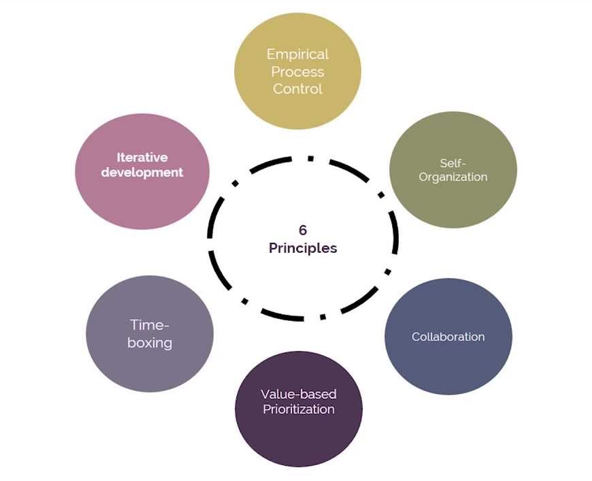
Scrum Principles

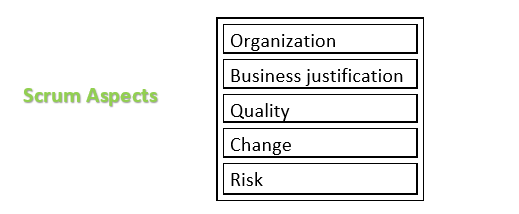
Scrum Aspects
The scrum aspects must be addressed and managed throughout a scrum project.
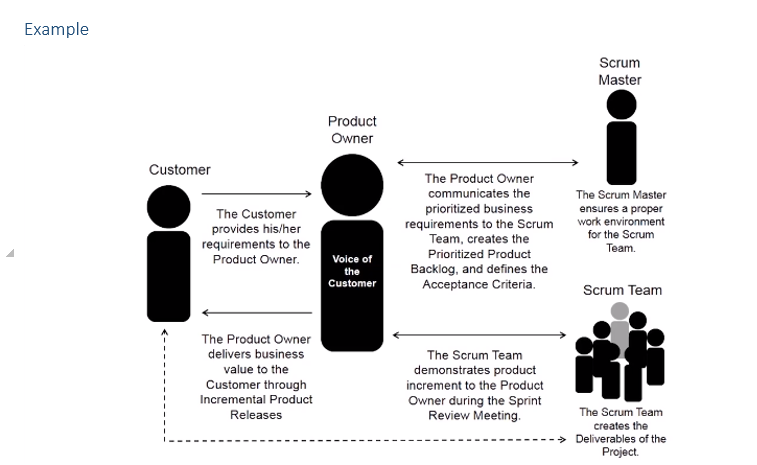
Three Main Scrum Roles

Product Owner
Responsible for achieving maximum business value for project.
Articulates customer requirements.
Maintain business justification for a project.
Scrum Master
Ensure that scrum team has an appropriate environment.
Guides, facilitates, and teaches scrum practices.
Clears impediments for the team.
Ensures that scrum processes are being followed.
Scrum Team
Responsible for understanding product.
Owner specified requirements.
Creating the project deliverables.
Key Scrum Aspect

Business justification concept in Scrum is based on the following
- Value-driven delivery
- Uncertainty of results or outcomes
- Impossible to guarantee projects success and completion
- Scrum attempts to start delivering results as early in the project as possible
- Provides an opportunity for reinvestment.
QUALITY: In scrum, quality is defined as the ability of the completed product or deliverables to meet the acceptance criteria and achieve the business value expected by the customer.
Scrum Processes
Scrum processes address the specific activities and flow to a scrum project. In total, there are 19 processes, which are grouped into 5 phases.
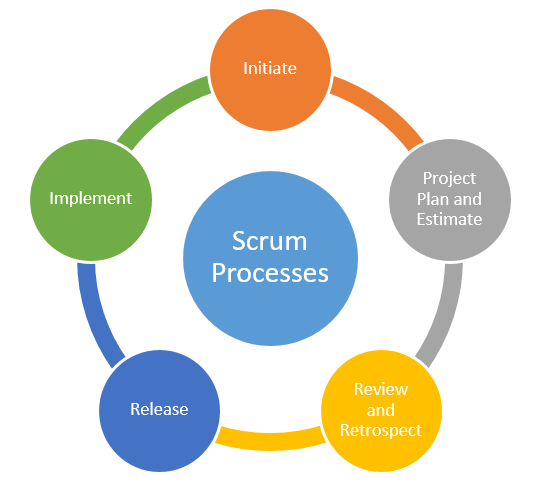
Here is a summary of the Scrum Framework
- The product owner creates a product backlog (essentially, a wishlist of tasks that need to be prioritized in a project)
- The Scrum team conducts a sprint planning session where the tasks necessary to complete items on the wishlist is broken down into small, more easily manageable chunks.
- The team creates a sprint backlog and plans its implementation.
- The team decides a time duration for every sprint. (the most common intervals is probably two weeks)
- The team gets together every day for a brief Scrum meeting (often referred to as a Daily Standup) where each member of the team shares daily updates, helping the team and the project manager assess the progress of the project.
- The Scrum Master guides the team and keeps them focused and motivated.
- The stakeholders and the product owner conduct a review at the end of each sprint.
Benefits of Scrum
Different stakeholders want different things from a software development process.
- Developers want to write code, not documents.
- Quality Assurance engineers want to create test plans that ensure product quality, and have high-quality code to test.
- Project Managers want a process that is easy to plan, execute, and track.
- Product Managers want features implemented quickly, with no bugs.
- Services and Support personnel want to know exactly what is in all product releases, and have a reliable means to satisfy customer requests for bug fixes and enhancements.
- Sales personnel want to know what is “in the pipeline” for future releases.
- Customers want all of their feature requests and bug-fixes done quickly.
- Executives, Program Managers, want to know exactly what is happening, and what is planned to happen.
- Everyone wants happy customers.
Advantages of Scrum
Here’s why the framework is so popular today:
- Scrum can help teams thorough project deliverables speedily and proficiently.
- Scrum guarantees effective use of time and money.
- Large projects are divided into easily convenient sprints.
- Developments are coded and tested during the sprint review.
- Works well for fast-moving development projects.
- The team gets clear visibility through scrum meetings.
- Scrum, being agile, adopts feedback from customers and stakeholders.
- Short sprints enable changes based on feedback a lot more easily
- The individual effort of each team member is visible during daily scrum meetings.
Disadvantages of Scrum
Nothing is perfect, and the Scrum methodology is no exception. However, like every framework, scrum also has few disadvantages.
In some cases, Scrum is combined with other project management techniques that can help resolve some of these drawbacks:
- Scrum often leads to scope creep, due to the lack of a definite end-date.
- The chances of project failure are high if individuals aren’t very committed or cooperative.
- Adopting the Scrum framework in large teams is challenging.
- The framework can be successful only with experienced team members.
- Daily meetings sometimes frustrate team members.
- If any team member leaves in the middle of a project, it can have a huge negative impact on the project.
- Quality is hard to implement until the team goes through an aggressive testing process.
Needless to say, proper planning and smart decision-making can help you get past these disadvantages with the Scrum methodology.
Conclusion
Scrum is designed to streamline team satisfaction and efficiency, product quality, responsiveness to clients, and transparency for stakeholders. The key practices that enable these advantages include de-emphasizing work on non-deliverable things, executing and completing each Story in a Sprint Backlog in rank request, working in short Sprints of 2-4 weeks, and making past, present, and future project information available to all stakeholders.
Reference:www.scrumstudy.com
Please share your kind feedback in the comments section. For any query, feel free to Contact us or email us on [email protected]